
#Calculus 2 practice final how to#
In particular, focus on how to identify whether a question requires a u-sub or by parts or a trig substitution, as they can look very similar at first glance. In particular, focus on u-substitutions, integration by parts, and trig substitutions / integrals, as they are some of the more challenging techniques. Integration Techniques – Be sure to practice the more complicated integration techniques as much as you can.If these are not given on a formula sheet (which often they are), you are going to want to simply memorize them. Trapezoidal Rule, etc), and how to apply them effectively. You will also want to remember the variations of the Reimann Sum (e.g. Reimann Sums / Integration – For this section you are going to want to remember the left, right and midpoint formulas to find areas under a curve.There many avenues that a student can pursue to get support for preparing for this exam, but for now, here are some tips and suggestions for things to focus on to help you with preparing for you Calculus 2 final exam: Studying for this exam can be challenging, given she sheer volume of problem types and techniques that you are required to understand and apply. Students in Calculus 2 (integral calculus) are preparing for their final exams in April.
#Calculus 2 practice final series#
Use the integral test to determine whether the following series converges or diverges.Are you prepared for your Calculus 2 exam? Determine whether the following series converges absolutely, converges conditionally or diverges. Determine whether the following series converges or diverges. Write a definite integral that represents the area inside the region enclosed by one loop DO NOTġ7. Give the coordinates of the points at which the curve crosses the axes. Find the the interval of convergence of the power series ∞∑ġ6.

Write a definite integral that gives the volume of the solid of revolution formed by revolving the region bounded by y = x3 + x + 1, y = 1, and x = 1 about the line x = 2.ġ5.
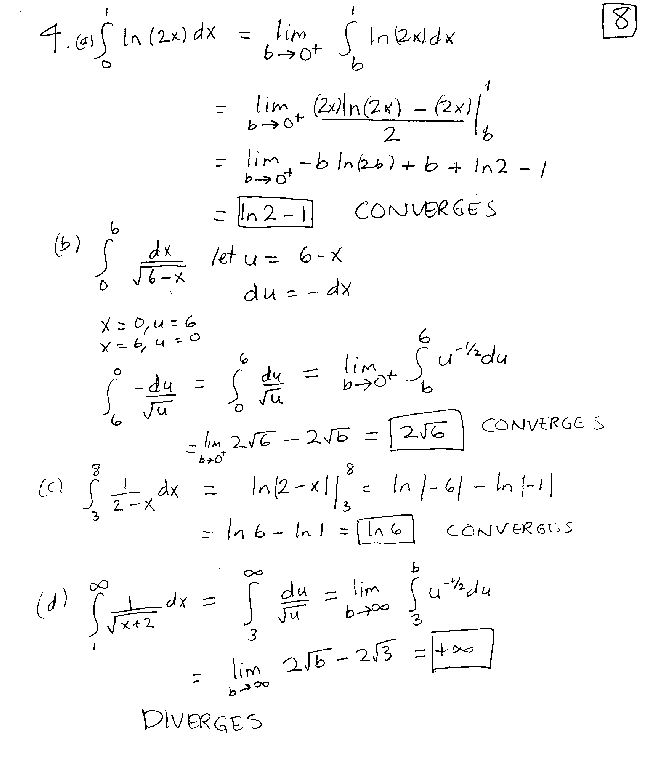
Write a definite integral that gives the volume of the solid of revolution formed by revolving the region bounded by the graph of x = e−yĪnd the y-axis between y=0 and y=1, about the x-axis.ġ4. Use a definite integral to express the length of the curve given by x = cos3 t, y = sin3 t, 0 ≤ t ≤ πġ3. Find the centroid of the region bounded by the curves y = x/2 and y = √ġ2. Write a definite integral that expresses the fluid force on the end of the tank when the oil is 4 feet deep?ġ1. The oil in the tank has a weight-density of 57 lb/ft3. Its height is 12 ft and width is 12 feet. A metal oil tank has cross-section that is a square rotated 45◦ as shown in the figure above. Express the volume of P as a definite integral. A solid figure P has R as a base region and cross-sections perpendicular to the x-axis are squares. Consider the region R bounded by y = 2x and y = x2. Integral does not converge, say so explicitly and show this.ĩ. (x + 1)1/3 + C to find the value of the following improper integrals, or, if an How much work does it take to pump the oil to the rim of the tank? Give your answer as a definite integral. It is filled to within 2 feet of the top with olive oil weighing 57 lb/ft3. A conical tank (shown below) has a height of 12 feet and the diameter of the top is 16 feet. (a) If y(t) is the amount of salt in the tank after t minutes, write down the initial value problem describing the mixing process: (b) Find y(t), the amount of salt in the tank after t minutes.ħ.

The mixture is kept uniform by stirring and flows out of the tank at the same rate of 5 gal/min. A brine containing 2 lb/gal of salt runs into the tank at the rate of 5 gal/min. A tank initially contains 100 gallons of brine in which 50 lb of salt are dissolved. Find a power series that represents the function 1Ħ. Find the slope of the line tangent to the parametric curve x = t cos t, y = 3t + t5 when t = 0.Ĥ.

What can you say about the signs of a, b, c?ģ. The function f(x), whose graph is shown, has the Taylor polynomial of degree 2 about x = 0 given by P2(x) = a + bx + cx2. (c) y = x2 + x is a solution to y′ = 2(y − x2) + 1 (c) T FĪkx k converges at x=1 and x=2 then it converges at x = -2. (b) If bn > 0 and bn+1 < bn then the series For each T/F question, write a careful and clear justification or describe a counterexample. If the statement is sometimes false, circle the printed capital F. For each part, if the statement is always true, circle the printed capital T. Practice Final Exam Math 1132 Spring 2009ġ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
